Few Americans Would Encourage a Young Person to Become a Teacher
Survey released during national teacher shortage finds perceptions of the profession as low-paying, stressful, and unsafe.
CHICAGO, Sept. 8, 2022 – Fewer than one in five Americans (18 percent) would encourage a young person to become a K-12 teacher, citing low pay, lack of sufficient school resources, and a stressful work environment as major barriers, according to NORC at the University of Chicago. These findings come amid a national teacher shortage and are from the latest NORC Spotlight on Education survey powered by AmeriSpeak®.

Spotlight On Education:
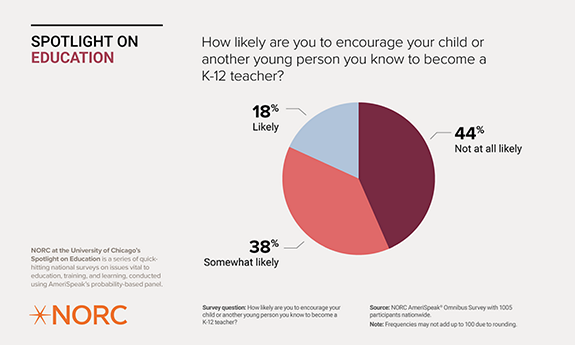
How likely are you to encourage pur child or another young person you know to become a K-12 teacher?
White and Wealthier Respondents Less Likely to Support Teaching as a Career Option
Of respondents, 44 percent are not at all likely to recommend going into teaching as a career path for young people. Looking at the data by race, white respondents are less supportive of a career in teaching, with 47 percent saying they are not at all likely to recommend becoming teachers, compared to 37 percent of respondents of color. By income, wealthier respondents are less likely to encourage a teaching career (50 percent of respondents with household incomes at or above $60,000), compared to respondents with household incomes below $60,000 (36 percent).
Low Pay, Lack of Resources, and Stressful Work Environment Seen as Major Barriers to Becoming a Teacher
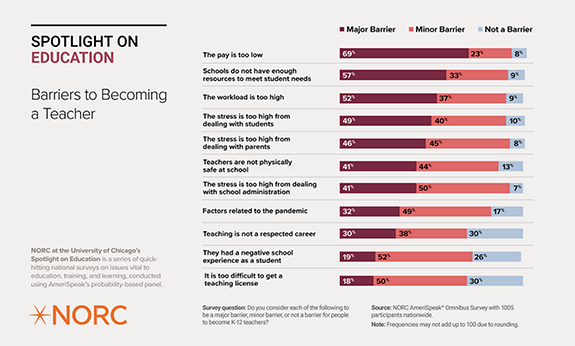
With nearly 300,000 open teaching positions in American public schools, policymakers are searching for ways to fill them. Over half of respondents believe that low teacher pay (69 percent), lack of school resources (57 percent), and high workload (52 percent) are major barriers to becoming a teacher. Nearly half of respondents also indicate that stress from dealing with students (49 percent), stress from dealing with parents (46 percent), and concerns for a teacher’s physical safety (45 percent) are major barriers.
“This poll echoes the common challenges school districts have had in hiring and retaining teachers for decades,” said Jenny Seelig, research scientist at NORC at the University of Chicago. “Concerns about teachers’ physical safety at work and factors related to the pandemic echo challenges for work environments beyond teaching.”

Spotlight On Education:
Barriers to Becoming a Teacher
Methodology
The self-funded poll was conducted between August 11 and 15 during a monthly Omnibus survey. It included 1,005 interviews with a nationally representative sample (margin of error +/- 4.16 percent) of adult Americans aged 18+ using the AmeriSpeak® Panel. Of note, percentages in the Barriers to Teaching graphic add up to less than 100 percent because of participants who selected “Other.” These participants represent less than 1 percent of overall participants in the study. AmeriSpeak is NORC’s probability-based panel designed to be representative of U.S. household populations. A comprehensive listing of all study questions, tabulations of top-level results for each question.
About the NORC Spotlight on Education
NORC’s Spotlight on Education is a series of quick-hitting national surveys on issues vital to education and its place in society, conducted using AmeriSpeak’s probability-based panel.
About NORC at the University of Chicago
NORC at the University of Chicago conducts research and analysis that decision-makers trust. As a nonpartisan research organization and a pioneer in measuring and understanding the world, we have studied almost every aspect of the human experience and every major news event for more than eight decades. Today, we partner with government, corporate, and nonprofit clients around the world to provide the objectivity and expertise necessary to inform the critical decisions facing society.
Contact: For more information, please contact Eric Young at NORC at young-eric@norc.org or (703) 217-6814 (cell).





